Classification
The most widely used classification of ovarian cancer is defined by FIGO (International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics). The current classification dates from 2013.
The stage participates in the evaluation of the prognosis of the disease (it is not the only parameter). He also participates in the choice of treatment.
Early stages :
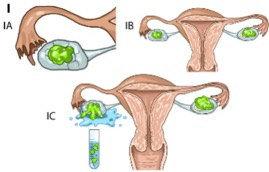
Stade Ia :
cancer limited to one ovary or fallopian tube. No tumor cells on the surface of the ovary or fallopian tube, nor in the peritoneum.Stade Ib :
cancer limited to both ovaries or both tubes. No tumor cells on the surface of the ovaries or fallopian tubes, nor in the peritoneum.Stade Ic :
cancer limited to one or two ovaries (one or two tubes)Ic1 : surgical rupture
Ic2 : preoperative rupture or tumor cells on the surface of the ovary or fallopian tube.
Ic3 : tumor cells in peritoneal lavage.
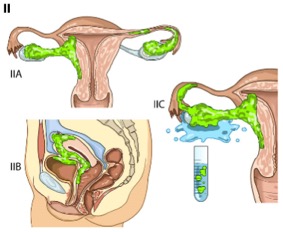
Stade IIa :
impairment of one or two ovaries (or tube) associated with pelvic extension under the upper strait (uterus, tube, ovary)Stades avancés :
Stade IIb :
extension to other pelvic organs.Stades III :
damage to the abdomen or lymph nodes.Stade IIIa :
lymph node or microscopic abdominal involvementStade IIIa1 :
isolated lymph node involvement (IIIa1i < 10mm ; IIIa1ii>10mm)Stade IIIa2 :
microscopic abdominal +/- lymph node involvementStade IIIb :
abdominal involvement< 2cm +/- ganglionnaireStade IIIc :
abdominal involvement > 2cm +/- lymph nodeStade IV :
Stade IVa :
pleural effusion with positive cytologyStade IVb :
parenchymal or extra-abdominal metastasis